There are many laws, principles, and guidelines that a UX designer can use to create user interfaces that are easy and enjoyable to use. In this article, we have listed laws of psychology for good UX design that will improve customer experience and user engagement.

These principles are widely used in UX Design and widely accepted by the designer community and will help you create an aesthetically pleasing design for a more pleasurable user experience, but please remember these are just guidelines, they are not strict laws and should be used with other design principles as well.
1. Fitts’ Law

Fitts’ Law, also known as the Index of Difficulty, is a principle of human-computer interaction. It states that:
The time it takes to accurately and comfortably select a target on a screen is a function of the distance to and size of the target.
Fitts’ Law for UI Design
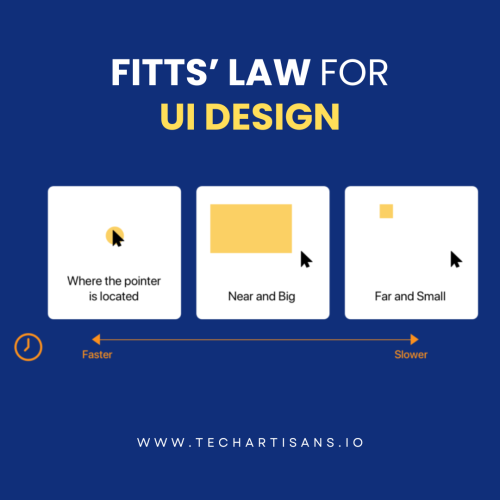
Fitts’ Law can be used to design elements that are easy and efficient for users to interact with.
For example, placing important buttons or links in larger and more prominent areas of the screen can reduce the time it takes for users to find and select them.
Consider reading more about effective web design in our article on the best web design software tool
Similarly, placing elements closer together can make users interact with them quickly and easily.
Applying Fitts’ Law in Your Website Design:
- Provide ample space between elements so users can easily select the one they want.
- Make frequently used buttons and links larger to reduce the time it takes for users to find them.
- Place important items closer to the user’s point of focus, such as the center of the screen.
- Use color, shape, or texture to make important elements stand out and be more easily selectable.
2. Hick’s Law

Hick’s Law, also known as the Hick-Hyman Law, is a principle of human-computer interaction that states:
The time users spend deciding increases as the number of choices grows.
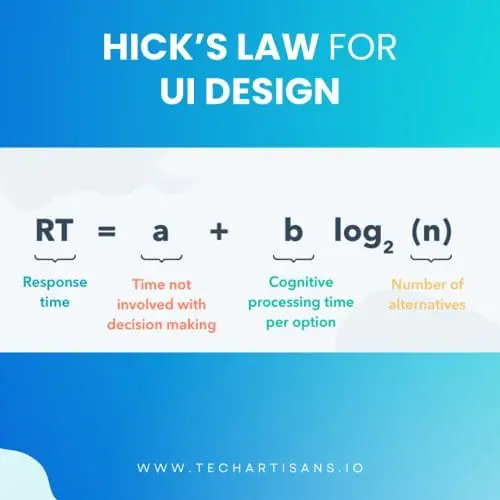
The Law states that the time (T) it takes to make a decision is a function of the number of choices (n) a person has.
Specifically, T = a log2 (n) + b, where a and b are constants.
Hick’s Law for UI Design
Hick’s Law can be used to design digital interfaces that make it easier for users to make decisions.
For example, by reducing the number of choices a user has to make, you can ensure users spend less time taking an action they want.
Learn about improving customer experience in our detailed guide on ways to improve customer experience
Similarly, by organizing choices into groups or categories, you can reduce the perceived number of options and make it easier for users to decide.
Applying Hick’s Law in Your Website Design
- Minimize the number of options presented to the user at one time.
- Organize opportunities into clear, meaningful categories or groups.
- Use progressive disclosure to reveal options only as they are needed.
- Use default options or preselections to reduce the votes the user needs to consider.
- Use clear and simple language to describe options.
3. Millar’s Law
Miller’s Law, also known as the “Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two,” is a principle of cognitive psychology that states:
The number of items a person can hold in their working memory at a time is around 7 +/- 2. This means that, on average, a person can save seven items in their working memory at one time, ranging between 5 and 9 items.
Miller’s Law for UI Design

Miller’s Law can be used to design interfaces that are easy and efficient for users to understand and use.
For example, by keeping the number of items on a screen or within a navigation menu to 7 or fewer, you can reduce the cognitive load on the user and make it easier for them to understand and use the interface.
Applying Miller’s Law in Your Website Design
Here are some ways you can apply Miller’s Law in your website design:
- Limit the number of items in a navigation menu or on a screen to 7 or fewer
- Group related items together in the navigation menu or on the screen
- Use clear and simple language to describe items.
- Use visual elements hierarchy to emphasize the most important items.
- Use progressive disclosure to reveal things only as they are needed.
Further insights can be found in our article on the laws of psychology for good UX design.
4. Weber’s Law

Weber’s Law is a principle of psychology that states:
The just-noticeable difference (JND) between two stimuli is a constant proportion of the original stimulus. The JND is often represented as a Weber fraction (ΔI/I) which describes the ratio of the change in stimulus intensity (ΔI) to the original intensity (I).
Weber’s Law for UI Design

By using a consistent visual hierarchy and contrast ratio throughout the website, you can make it easy for users to distinguish between different types of information and elements on the screen.
Similarly, by providing feedback proportional to the user’s actions, you can make it easy for users to understand the results of their actions.
Applying Weber’s Law in Your Web Design
Here are some ways you can apply Weber’s Law in your website design:
- Use consistent visual hierarchy and contrast ratio throughout the website.
- Use proportional feedback for user actions.
- Use clear and consistent typography and iconography.
- Use progressive disclosure to reveal elements gradually to the user.
- Use clear and consistent color coding to distinguish elements.
Discover more in our article about UX and web design differences
5. The Serial Position Effect
The Serial Position Effect is a principle of cognitive psychology that states:
People remember the first and last items in a series better than those in the middle.
The phenomenon is often referred to as the primacy effect (for items at the beginning of the list) and the recency effect (for items at the end of the list).
The Serial Position Effect For the UI Design
The serial position effect can be used to design interfaces that are easy for users to navigate and remember.
For example, by placing important items at the beginning or end of a list, you can make users more likely to remember them.
Similarly, using clear and consistent labels or headings can make it easier for users to remember the items in the middle of a list.
Applying for the Serial Position in Your Web Design
Here are some ways you can apply the serial position effect in your website design:
- Place important items at the beginning or end of a list.
- Use clear and consistent labels or headings to help users remember items in the middle of a list.
- Use a clear visual hierarchy to emphasize important items.
- Use clear and consistent typography and iconography to distinguish items.
- Use clear and consistent color coding to distinguish items.
Explore our piece on how to create user flow for more related information.
6. The Von Restorff Effect

Also known as the “isolation effect,” Von Restorff Effect is a principle of cognitive psychology that states:
Users prefer items that stand out in some way. They are more likely to be remembered than items that are similar to those around them.
This effect is named after the German psychologist Hedwig von Restorff, who first demonstrated it in a study in 1933.
The Von Restorff Effect On the UI Design
The Von Restorff effect can be used to design interfaces that are easy for users to navigate and remember.
For example, by making important items stand out in some way, such as using a different color, shape, or size, you can make users more likely to remember them.
Similarly, you can make them more memorable by isolating important items from their surroundings, such as placing them in a different location or giving them more space.
Applying the Von Restorff In Your Website Design
Here are some ways you can apply the Von Restorff effect in your website design:
- Make important items stand out by using a different color, shape, or size
- Isolate important items from their surroundings by placing them in a different location or giving them more space.
- Use clear and consistent typography and iconography to distinguish items.
- Use clear and consistent color coding to distinguish items.
- Use animations and other visual effects to draw attention to important items.
Refer to our article on template vs custom website design for additional insights.
7. The Recognition Principle

The Recognition Principle is a cognitive bias that suggests that:
People tend to feel more positive toward familiar things.
Applying The Recognition Principle on a Website
This principle can be applied to improve the user journey on website visitors in several ways:
- Ensure your website’s branding is consistent across all pages and elements, such as logos, colors, and fonts so that the visitors recognize your brand and feel familiar with it.
- Offer customized recommendations based on things users have interacted with previously, such as recently viewed products or similar content to make visitors feel recognized and valued.
- Use clear and intuitive navigation that visitors can easily recognize and understand so they feel more comfortable using it.
- Use interfaces and multiple similar objects elements familiar to visitors, such as standard icons or buttons.
- Use ads to show visitors familiar products or services they’ve recently viewed on your website to keep your brand top of mind and increase the likelihood of a conversion.
Learn more about enhancing user experience in our discussion on user experience and SEO
8. The Continuity Principle
The Continuity Principle is a cognitive bias that suggests that:
People perceive things that form a continuous pattern or sequence as more coherent than unrelated.
The Continuity Principle for UX Design

This principle can be applied to improve the user experience for website visitors in several ways.
For example, it helps with easy navigation, branding, and ensuring that the user experience is consistent throughout the website, such as using the same navigation menu on all pages.
Applying The Consistent Layout for the Website
- Use a consistent layout throughout the website, such as using the same grid system or template. It helps visitors understand the website’s overall structure and makes navigating it easier.
- Use consistent branding throughout the website, using the same logo, colors, and fonts. It allows visitors to recognize and remember your brand, making it more likely that they will return.
- Use consistent messaging throughout the website, such as using the same tone and voice that represents your brand personality and creates a sense of continuity.
- Ensure that the user experience is consistent throughout the website, such as using the same navigation menu on all pages. This helps visitors understand how to interact with the website and reduces the learning curve.
See our article on how to choose a web hosting provider for more related content.
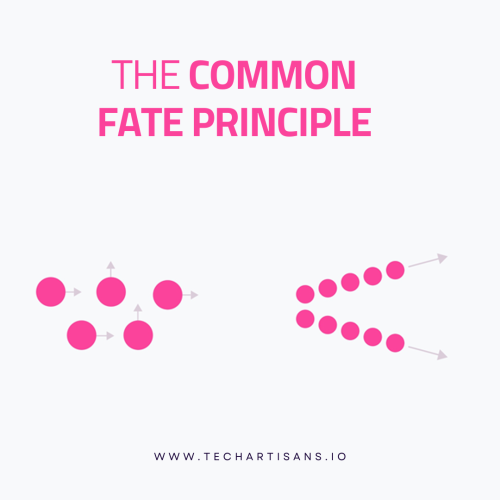
9. The Common Fate Principle
The Common Fate Principle is a cognitive bias that suggests that:
People tend to perceive elements that move or change together as related.
Applying The Common Fate Principle to Your Website
This principle can be used to improve the user experience for website visitors in several ways:
- Use animations to create a sense of common fate, such as animating related elements to make the website more interactive and engaging.
- Use visual cues to create a sense of common fate, such as using arrows or lines to connect related elements and reduce confusion.
- Use consistent transitions between different states or pages, such as using the same animation for page transitions to create a sense of continuity and help visitors understand the relationships between other pages.
- Use interactive elements to create a sense of common fate between the user and the website, such as hover effects or click animations.
Our article on hero images that drive conversions may provide further relevant insights.
10. Jakob’s Law
Jakob’s Law of UX states that:
Users spend most of their time on other sites, and they prefer your site to work the same way as those other sites.
This means that users are accustomed to certain conventions and patterns in website design and user experience, and they expect those patterns to be followed on other websites as well.
Jakob’s Law For the UI Design
This law is important in UI design because it highlights the importance of designing a website that is familiar and easy to use for users.
By following established conventions and patterns on all the other sites, you can create a user-friendly website that is intuitive and easy to navigate.
If your website deviates too much from what users are used to, they may become frustrated or confused, which can lead to a negative user experience and lost conversions.
Applying Jakob’s Law on the Website
To apply Jakob’s Law while designing a website, you should:
- Research existing websites in your industry to identify common design patterns and user expectations.
- Use those patterns and expectations as a basis for your own design, while also incorporating your brand’s unique style and personality.
- Conduct user testing to ensure that your design is intuitive and easy to use for your target audience.
- Continuously iterate and improve your design based on user feedback and analytics data to ensure that you are meeting users’ expectations and providing a positive user experience.
For more on making your site user-friendly, see our piece on UX vs UI design
Conclusion
Incorporating certain psychological principles into UX design can significantly improve the user’s experience.
By understanding how people perceive and interact with digital products, UX designers can create interfaces that are intuitive, engaging, and effective. By implementing these principles, designers can create products that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and easy to use.
Ultimately, good UX design is about understanding the user’s needs and creating interfaces that facilitate their goals and objectives.
Read about how effective ways to measure your brand awareness can influence UX design.